Description
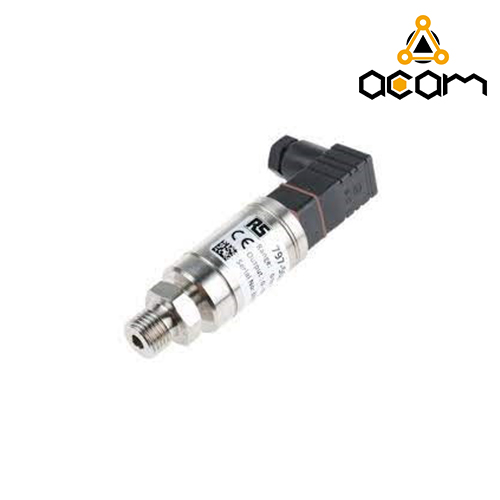
The pressure sensor is one of the fundamental factors that must be considered and measured in various industrial operations. Given the high importance of this parameter, a specific instrument has been developed for its measurement. The pressure sensor, also referred to as a pressure transmitter, is utilized for this purpose. In the following sections of the article, we will discuss in greater detail the functioning of this product, its types, and its applications.
What is a Pressure Sensor?
In simple terms, a pressure sensor is a device responsible for controlling the pressure exerted on an apparatus. This instrument converts a mechanical function (pressure) into an analog electronic signal. The electronic pressure sensor can be indirectly used to measure other parameters as well. Flow rate, velocity, liquid level, and height are among these parameters. If you are interested, you can read the article on signal lights for further information.
Types of Industrial Pressure Sensors
Industrial pressure sensors can be categorized into various types. There are several factors involved in this classification, each leading to different subdivisions of pressure sensors. Understanding these classifications is vital, as choosing an inappropriate pressure transmitter for a specific operation can deliver incorrect information, potentially causing significant harm to the process. In the following sections, we will first investigate the kinds of pressure that this device is capable of measuring and then delve into an alternative method of categorizing pressure sensors.
Types of Reference Pressure
Generally, the pressures that these measurement devices are designed to gauge can be categorized into three distinct classes:
Absolute Pressure
Absolute pressure refers to the measurement type where the secondary side of the diaphragm in an absolute pressure sensor is situated in a vacuum. Consequently, the deformation corresponds exactly to the magnitude of the pressure being assessed.

Relative Pressure
In sensors that measure this form of pressure, the opposing side of the diaphragm faces atmospheric pressure. Thus, the pressure that is measured reflects the difference between the atmospheric pressure and the applied force exerted.

Differential Pressure
In a differential pressure sensor, both input points of the diaphragm are aligned on the same side. The value that is displayed is the result of the difference in pressure between these two inputs.

Types of Pressure Sensors Based on Functionality
In addition to the type of reference pressure, the functionality of these devices can also be considered a criterion for categorizing pressure sensors. Below, you will find some of the most prominent types of pressure sensors based on their operation:
• Strain Gauge piezoresistor
• Capacitive Pressure Sensor
• Electromagnetic Pressure Sensor
• Piezoelectric Sensor
• Optical Pressure Sensor
• Potentiometric Pressure Sensor
• Resonant Pressure Sensor
• Temperature-Based Pressure Sensor
• Hot-filament ionization gauge
It should be noted that there are other factors based on which these tools can be categorized. If you have encountered terms like electronic pressure sensor or digital pressure sensor in the market, these classifications refer to criteria such as the structure and design of the device.
Applications of Pressure Sensors
The direct application of this tool, as can be inferred from its name, is evident and doesn’t require extensive discussion. However, this product has other uses as well, some of which we will mention below.

Determining Altitude Above Sea Level
The determination of altitude above sea level is one of the indirect applications of this device. However, this functionality is limited to a specific height range (up to 11,000 meters) and is not applicable beyond that altitude. This technology is utilized in various fields, such as airplanes, rockets, weather balloons, and more.
Measuring Flow
Taking the Venturi effect into consideration, along with its correlation to pressure, it is possible to gauge the flow rate.
Measuring Height and Depth
Specific formulas enable the use of pressure sensors to measure the height of liquid surfaces, expanding their applications. This function is particularly valuable for determining the position of objects submerged in water, such as divers and submarines. Additionally, it can be used to gauge the elevation level inside a container, contributing to precise control in industrial processes.
Detection of Leakage
If it becomes feasible to measure pressure drop, this factor can be utilized to discern the presence or absence of leakage within a system. This assessment can be conducted by comparing the pressure of one system with that of another system known to have a specific leak or by measuring the pressure of a system at various time intervals and comparing these values with each other. For further exploration, you may refer to the enclosed plastic cover study.
Special Applications of Pressure Transmitters
You may occasionally wonder, “What is a pressure transmitter?” A pressure transmitter is essentially a pressure sensor, and in addition to the applications mentioned earlier, the use of a pressure transmitter holds a distinct place in certain areas. Cooling systems, mobile phones, factories, and workshops with industrial electricity are among the prevalent places where pressure sensors are utilized.
Essential Considerations in Selecting a Pressure Sensor
When purchasing a pressure transmitter, certain considerations should be taken into account, which may lead to cost savings in the purchase price. However, keeping these points in mind might result in acquiring a sensor at a higher price, but the cost of the pressure sensor could reduce your future expenses. When purchasing a pressure sensor, it is advisable to consider the following factors to make the best selection:
• Desired pressure range
• Type of pressure to be measured
• Required output
• Necessary accuracy for the sensor
• Display resolution
• Transmitter’s life cycle
• Connection processes
• Environmental conditions
• Temperature compensation
• Chemical compatibility
• Technical support





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.